In this example we connect a TM1637 quad 7-segment LED display driver module to a TPyboard, in this case we I used a TPyboard 202
and this was the 7 segment display display
Description
A common display module that you can buy on the internet contain the Tm1638 driver chip, I was interested in this one which is the TM1637 which appears to be a more basic version which can only control a display, the TM1638 can also control LED’s, buttons and two displays at the same time.
This is a common anode 4-digit tube display module which uses the TM1637 driver chip; Only 2 connections are required to control the 4-digit 8-segment display
Features of the module
Display common anode for the four red LED
Powered supply by 3.3V/5V
Four common anode tube display module is driven by IC TM1637
Can be used for Arduino devices, two signal lines can make the MCU control 4 8 digital tube. Digital tube 8 segment is adjustable
Here is how to hook the module up, the good news is this worked with my LOLIN32 and 3.3v
Parts Required
| Name | Link |
| TM1637 LED Display Module | TM1637 LED Display Module 7 Segment 4 Bits 0.36Inch Clock RED Anode Digital Tube Serial Driver Board Pack for arduino Diy Kit |
| TPYBoard V202 | TPYBoard V202 Pyboard Micropython Development Board |
| Connecting cables | Free shipping Dupont line 120pcs 20cm male to male + male to female and female to female jumper wire |
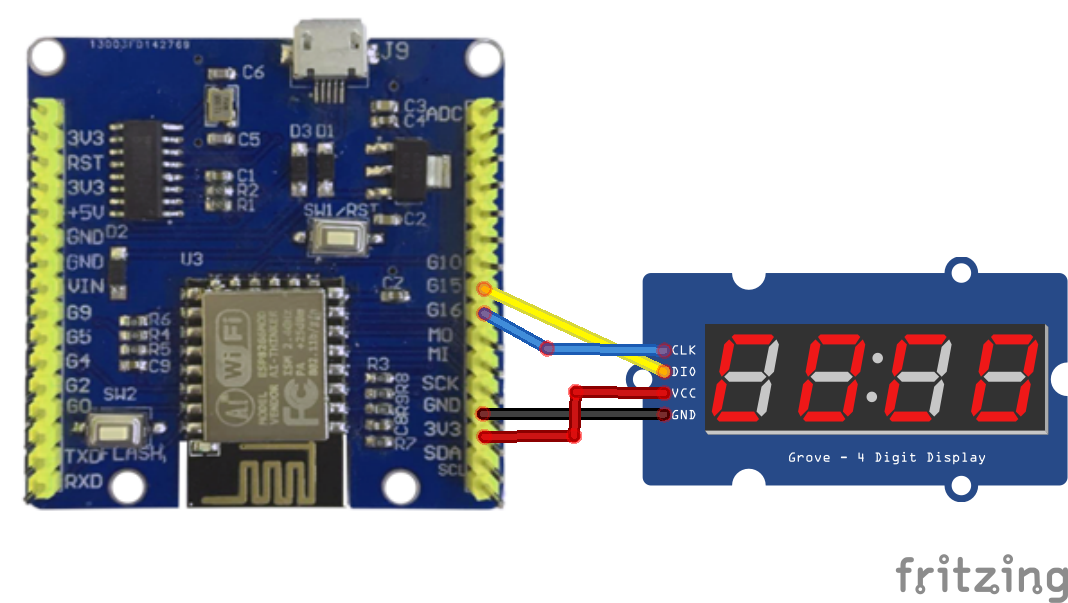
Schematic/Connection
Code Example
I used Mu for development, you can use the TM1637 library from https://github.com/mcauser/micropython-tm1637
I used uPycraft and copied the library to the uPylib folder on my PC at C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\uPyCraft\examples\uPy_lib, then I copied it from that folder to my device.
This is a test example in the library which pretty much highlights all of the functionality, you can also use any other Micropython supported board
[codesyntax lang=”python”]
import tm1637
from machine import Pin
tm = tm1637.TM1637(clk=Pin(16), dio=Pin(15))
# all LEDS on "88:88"
tm.write([127, 255, 127, 127])
tm.write(bytearray([127, 255, 127, 127]))
tm.write(b'\x7F\xFF\x7F\x7F')
tm.show('8888', True)
tm.numbers(88, 88, True)
# all LEDS off
tm.write([0, 0, 0, 0])
tm.show(' ')
# write to the 2nd and 3rd segments only
tm.write([119, 124], 1) # _Ab_
tm.write([124], 2) # __b_
tm.write([119], 1) # _A__
# display "0123"
tm.write([63, 6, 91, 79])
tm.write(bytearray([63, 6, 91, 79]))
tm.write(b'\x3F\x06\x5B\x4F')
tm.show('1234')
tm.number(1234)
tm.numbers(12, 34, False)
# display "4567"
tm.write([102, 109, 125, 7])
tm.write([102], 0) # 4___
tm.write([109], 1) # _5__
tm.write([125], 2) # __6_
tm.write([7], 3) # ___7
# set middle two segments to "12", ie "4127"
tm.write([6, 91], 1) # _12_
# set last segment to "9", ie "4129"
tm.write([111], 3) # ___9
# walk through all possible LED combinations
from time import sleep_ms
for i in range(128):
tm.number(i)
tm.write([i])
sleep_ms(100)
# show "AbCd"
tm.write([119, 124, 57, 94])
tm.show('abcd')
# show "COOL"
tm.write([0b00111001, 0b00111111, 0b00111111, 0b00111000])
tm.write([0x39, 0x3F, 0x3F, 0x38])
tm.write(b'\x39\x3F\x3F\x38')
tm.write([57, 63, 63, 56])
tm.show('cool')
tm.show('COOL')
# display "dEAd", "bEEF"
tm.hex(0xdead)
tm.hex(0xbeef)
tm.show('dead')
tm.show('Beef')
# show "12:59"
tm.numbers(12, 59)
tm.show('1259', True)
# show "-123"
tm.number(-123)
tm.show('-123')
# Show Help
tm.show('Help')
tm.write(tm.encode_string('Help'))
tm.write([tm.encode_char('H'), tm.encode_char('e'), tm.encode_char('l'), tm.encode_char('p')])
# Scroll Hello World from right to left
tm.scroll('Hello World') # 4 fps
tm.scroll('Hello World', 1000) # 1 fps
# Scroll all available characters
tm.scroll(list(tm1637._SEGMENTS))
# all LEDs dim
tm.brightness(0)
# all LEDs bright
tm.brightness(7)
# converts a digit 0-0x0f to a byte representing a single segment
# use write() to render the byte on a single segment
tm.encode_digit(0)
# 63
tm.encode_digit(8)
# 127
tm.encode_digit(0x0f)
# 113
# 15 or 0x0f generates a segment that can output a F character
tm.encode_digit(15)
# 113
tm.encode_digit(0x0f)
# 113
# used to convert a 1-4 length string to an array of segments
tm.encode_string(' 1')
# bytearray(b'\x00\x00\x00\x06')
tm.encode_string('2 ')
# bytearray(b'[\x00\x00\x00')
tm.encode_string('1234')
# bytearray(b'\x06[Of')
tm.encode_string('-12-')
# bytearray(b'@\x06[@')
tm.encode_string('cafe')
# bytearray(b'9wqy')
tm.encode_string('CAFE')
# bytearray(b'9wqy')
tm.encode_string('a')
# bytearray(b'w\x00\x00\x00')
tm.encode_string('ab')
# bytearray(b'w|\x00\x00')
# used to convert a single character to a segment byte
tm.encode_char('1')
# 6
tm.encode_char('9')
# 111
tm.encode_char('-')
# 64
tm.encode_char('a')
# 119
tm.encode_char('F')
# 113
# display "dEAd", "bEEF", "CAFE" and "bAbE"
tm.hex(0xdead)
tm.hex(0xbeef)
tm.hex(0xcafe)
tm.hex(0xbabe)
# show "00FF" (hex right aligned)
tm.hex(0xff)
# show " 1" (numbers right aligned)
tm.number(1)
# show " 12"
tm.number(12)
# show " 123"
tm.number(123)
# show "9999" capped at 9999
tm.number(20000)
# show " -1"
tm.number(-1)
# show " -12"
tm.number(-12)
# show "-123"
tm.number(-123)
# show "-999" capped at -999
tm.number(-1234)
# show "01:02"
tm.numbers(1, 2)
# show "0102"
tm.numbers(1, 2, False)
# show "-5:11"
tm.numbers(-5, 11)
# show "12:59"
tm.numbers(12, 59)
# show temperature '24*C'
tm.temperature(24)
tm.show('24*C')
# show temperature works for range -9 to +99
tm.temperature(-10) # LO*C
tm.temperature(-9) # -9*C
tm.temperature(5) # 5*C
tm.temperature(99) # 99*C
tm.temperature(100) # HI*C
[/codesyntax]
Output






